Gene Therapy for Advanced Dry AMD
Phase I/II study generating positive data for treatment designed to restore homeostatic balance to the complement system.

Cheryl Guttman Krader
Published: Wednesday, August 31, 2022
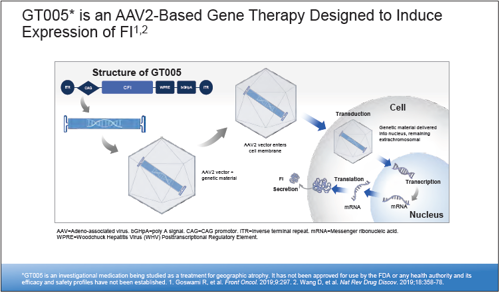
Preliminary results from the phase I/II FOCUS study suggest subretinally delivered GT005—a recombinant adenoassociated viral (AAV2) vector encoding Complement Factor I (CFI)—could offer a onetime gene therapy for geographic atrophy (GA) secondary to age-related macular degeneration (AMD), said Jared S Nielsen MD, MBA.
“Although injection of agents that inhibit C3 or C5 has shown to slow GA progression, these treatments demand burdensome ongoing injections and display sawtooth pharmacodynamics, which may not be the best way to interact with the complement system,” said Dr Nielsen.
“GT005 is designed to induce expression of CFI, which acts as a key downregulator of complement. Instead of inhibiting the complement pathway, the rationale for GT005 is to modulate some of the key regulatory proteins in the complement cascade to restore a homeostatic balance with a one-time intervention that will have a continuous and durable effect to hopefully prevent the development or progression of AMD.”
FOCUS is an open-label multicentre study, evaluating subretinal delivery via two different approaches—a transvitreal approach and a suprachoroidal cannulation approach using the Orbit Subretinal Delivery System. It includes dose-escalation and dose-expansion cohorts for both delivery approaches.
Eligible patients have bilateral GA. The study is evaluating safety data at 48 weeks for the primary outcome. Secondary efficacy endpoints for analysis include anatomic and functional measures as well as changes in vitreous biomarkers for complement expression.
Dr Nielsen presented safety data for the first 31 enrolled patients and biomarker data from 13 patients. The patients were all treated with the transvitreal delivery and represented 11 patients enrolled in the dose-escalation phase and 20 in the dose expansion cohort. Dr Nielsen reported the treatment was well tolerated so far. No serious adverse events or laboratory safety signals have been seen.
There were 31 treatment-emergent adverse events in the study eye, of which 20 were mild. Changes in the RPE (5 mild, 1 moderate) that were restricted to the bleb area and not accompanied by significant visual changes were noted in some patients who received the highest dose of GT005.
Encouragingly, GT005 has so far demonstrated a benign immunogenicity profile. There were no signs of GT005-related inflammation, no antibodies to CFI detected, and the vector shedding profile aligns with other recombinant AAV ocular therapies, Dr Nielsen said.
Analyses of intraocular fluid samples showed increased CFI in the vitreous that was mirrored by increased aqueous levels of the protein along with downstream modulation of complement biomarkers consistent with reduced complement activity.
“The increase in CFI in the aqueous is something we would expect in vitrectomised eyes and suggests the possibility of monitoring intraocular CFI by sampling the aqueous,” said Dr Nielsen.
“The observed changes in biomarkers of the complement system suggest that GT005 is not only inhibiting the downstream effects of the complement pathway, but it is also affecting the amplification or upregulation and decreasing parental C3, and that is exciting.”
Dr Nielsen presented these findings at ARVO 2022 in Denver, Colorado, US.
Jared S Nielsen MD, MBA is Director of Retina Clinical Research, Director of the Retina Fellowship Training Program, and based at the Wolfe Eye Clinic, West Des Moines, Iowa, US. jnielsen@wolfeclinic.com
Latest Articles
Simulators Benefit Surgeons and Patients
Helping young surgeons build confidence and expertise.
How Many Surgeries Equal Surgical Proficiency?
Internet, labs, simulators, and assisting surgery all contribute.
Improving Clinical Management for nAMD and DME
Global survey data identify barriers and opportunities.
Are Postoperative Topical Antibiotic Drops Still Needed?
Cataract surgeons debate the benefits of intracameral cefuroxime prophylaxis.
Emerging Technology for Detecting Subclinical Keratoconus
Brillouin microscopy shows promise in clinical studies.
Knowing Iris Repair: Modified Trifold Technique
Part eight of our series covers the modified trifold technique for large iris defects.
It’s All About Biomechanics!
Increasing the pool of patients eligible for refractive surgery.
Uncovering More Safe and Quick Options
Different strategies, such as PresbyLASIK, can offer presbyopes good outcomes.
Topography-Guided PRK for Keratoconus
Improving visual acuity in patients with keratoconus.
Defining AMD Treatment Protocol
Treatments trending to fewer injections for better results.